Detection of Adversarial Devices using Machine Learning
目录
1. A Systematic Review of Data-Driven Attack Detection Trends in IoT #
Objectives:
This research aims to provide an overview of the IoT datasets available today, trends in machine learning and deep learning usage, and the efficiencies of these algorithms on a variety of relevant datasets. The results of this comprehensive survey can serve as a guide and resource for identifying the various datasets, experiments carried out and future research directions in this field.
Index: IoT; datasets; machine learning; cyberattack; intrusion detection; threat detection
Methods:
- Define the research questions (RQs) the review addresses.
- Outline the information sources used to retrieve relevant information.
- Determine the keywords used to perform search queries in the databases.
- Filter of information based on inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- Representation of the results found in relation to the research questions defined
Main Context:
iot architecture and threat mapping
mindmap root((IoT Architecture)) A[Layer Specific] Physical Network Middleware Application Domain Specific Cloud IoT IIoT Smart Cities Industriy Specific Smart things Cisco AWSDatasets and corresponding networks


Dataset Features:
3 features are mainly used for tagging benign, attack and type of attack: attack, category and subcategory labels
e.g. the category is used to indicate that a flow belongs to a DoS attack while the subcategory indicates if it was a UDP, TCP, HTTP or ICMP DoS attackAttack category:
OSI mapping:Layer Attack application XSS, SQL injection, HTTP DoS transport TCP, UDP, DDoS, DoS Network ICMP flood, DoS Datalink ARP Spoofing Traffic Related: Mirai and BASHLITE are the most common types DoS and reconnaissance attacks are the next most common
IoT protocols related: MQTT attacksML and DL tools:
It was also observed that the most commonly used ML algorithms were tree-based, while neural networks (NNs) are the most common for DL algorithms.Federated Learning: data from iot are non-IID, device could train the model at different times with different data sizes or parameters. This is a huge advantage, as IoT sensors differ in terms of their characteristics and the amount of information they gather.
Outcomes:
feature engineering, IoT protocols, system requirements and efficiencies of detection models
Contribution:
A foundation for understanding the current state and potential trajectory of data-driven attack detection trends in IoT research. The variations within the range of IoT-related datasets studied demonstrate that momentum is building in this area.
2. CICIoT2023: A Real-Time Dataset and Benchmark for Large-Scale Attacks in IoT Environment #
Objectives:
The main goal of this research is to propose a novel and extensive IoT attack dataset to foster the development of security analytics applications in real IoT operations.
To accomplish this, 33 attacks are executed in an IoT topology composed of 105 devices. These attacks are classified into seven categories, namely DDoS, DoS, Recon, Web-based, brute force, spoofing, and Mirai. Finally, all attacks are executed by malicious IoT devices targeting other IoT devices.
Index: Internet of Things (IoT); dataset; security; machine learning; deep learning; DoS; DDoS; reconnaissance; web attacks; brute force; spoofing; Mirai
Methods:
IoT topology -> execute attacks -> collect data from benign and malicious scenarios
Main Context:
Data collection of benign and malicious scenarios:
Attack DDoS ACK Fragmentation, UDP Flood, SlowLoris, ICMP Flood, RSTFIN flood, PSHARK flood, HTTP Flood, UDP Fragmentation, ICMP fragmentation, TCP Flood, SYN Flood, SynonymousIP Flood DoS TCP Flood, HTTP Flood, SYN Flood, UDP Flood Recon Ping Sweep, OS Scan, Vulnerability Scan, Host Discovery Web-Based SQL injection, command injection, Backdoor Malware, Uploading Attack, XSS, Browser Hijacking Brute Force Dictionary Brute Force Spoofing ARP Spoofing, DNS Spoofing Mirai GREIP Flood, Greeth Flood, UDPPlain Gathering info from the iot topology Ping Sweep, OS Scan, Vulnerability Scan, Port Scan, Host Discovery
Evaluation: Logistic Regression, Percepton, AdaBoost, DeepNeuralNetwork, Random Forest
Outcomes:
We evaluate ML performance from three different perspectives:
- multiclass classification, focussing on classifying 33 individual attacks;
- grouped classification, considering 7 attack groups (e.g., DDoS and DoS);
- binary classification (i.e., malicious and benign traffic classification)
Contribution:
- Design a new realistic IoT attack dataset, CICIoT2023, using an extensive topology composed of several real IoT devices acting as either attackers or victims;
- We perform, document, and collect data from 33 attacks divided into 7 classes against ioT devices and demonstrated how they can be reproduced;
- We evaluate the performance of machine and deep learning algorithms using the CICIoT2023 dataset to classify and detect IoT network traffic as malicious or benign.
3. Reinforcement learning meets network intrusion detection: a transferable and adaptable framework for anomaly behavior identification #
Objectives:
Most anomaly detection model must train the entire data set at an immense cost. We propose a transferable and adaptable network intrusion detection system(TA-NIDS) based on deep reinforcement learning.
Index: Deep reinforcement learning, anomaly detection, transferable framework, robustness, adaptable framework
source code:
https://github.com/HE0413/TA-NIDS.git
Methods: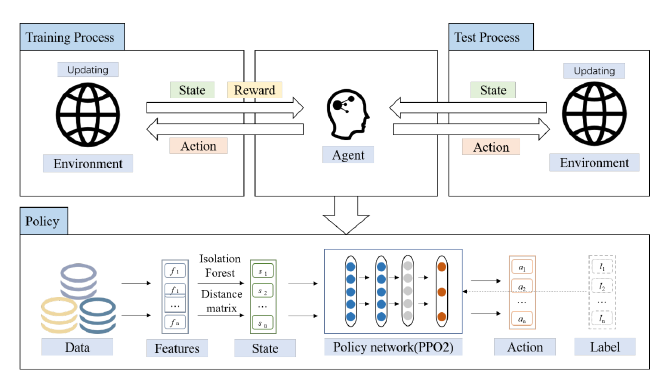
- Basic RL: The agent obtains knowledge from the environment and improves the action plan to adapt to the environment. Positive reward is regarded as the reinforcement signal, try to maximize the expectation of reward R_t.
- Reward machanism for interactive processes: set the positive reward that can be obtained only when outlier classes are screened correctly. Prioritize selecting outliers by reward mechanism, making it adaptable to the actual scene.
- Proximal policy optimization(PPO): PPO uses constraints to ensure that the difference between the old and new strategies is not too significant, which can avoid unexpected performance degradation caused by significant differences.
Main Context:
- prioritize key categories: a large data set may only have a few outliers. Apparent outliers must be selected first.
- Interaction between agent and environment: RL obtains valuable information with the reward through continuous interaction.
- Identify a general data format: which can calculate the features of different data sets
- Detailed design: Enviroment, State, Action, Reward, Policy
Outcomes:
- Datasets:
Dataset Attributes attacks IDS2017 Contain benign and common attacks brute force FTP, SSH, DOS, Heartbleed, Web attack, Intrusion, Botnet, and DDoS IDS2018 network traffic and system logs brute force, Heartbleed, Botnet, DOS, DDoS, Web NSL-KDD UNSW-NB15 comprehensive network attack traffic dataset 49 features and 9 attacks. Fuzzers, Analysis, Backdoors,DOS, Exploits, Generic, Reconnaissance, Shellcode, and worms CIC-IoT ioT network traffic dataset seven categories: DDoS, DoS, Recon, Web-based, Brute Force, Spoofing, and Mirai - Experiments on data sets including binary classification, multiple classifications and transferable results.
Contribution:
- Propose a framework for anomaly detection with adaptability and transferability based on deep reinforecement learning(DRL).
- Transferability: Unify the features of the data set into the states observed from the environment. No requirements for feature dimensions, no need to adjust parameters.
- Adaptability and robustness: Design a reward mechanism to allow the agent to preferentially select ouliers, prioritizing the selection of outliers improves detection efficiency.
- Designed an enviroment that adjusts based on the identification action, and the states can be calculated using input network traffic, where transforming the traffic characteristics into the state in the environment. The environment has interaction with the agent, changes in real time.
- Conduct extensive experiments in IDS2017, IDS2018, NSL-KDD,UNSW-NB15, CIC-IoT2023
- TA-NIDS suits the following scenarios related to network security management:
- Scenes where noticeable abnormalities must be detected first.
- Scenes in which the natural environment changes in real time.
- Transfer the results of one data set directly to other data sets.